The Gender Pay Gap in Soccer: A Closer Look at the Earnings of Male and Female Players
Soccer, like many other sports, has been plagued by issues of gender inequality, particularly when it comes to pay. While some progress has been made towards closing the gap, there is still a significant difference between what male and female players earn. In this article, we take a closer look at the earnings of male and female soccer players, and explore what is being done to address this issue.

The Gender Pay Gap in Soccer:
According to a report by Forbes, the top 10 highest-paid male soccer players earned a combined $652 million in 2022. That’s an average of $65million per player. In contrast, the top 10 highest-paid female soccer players earned a combined $3.2 million in the same year, which works out to an average of $320,000 per player. That’s a staggering difference of $65.7 million per player, or a 200-fold difference.
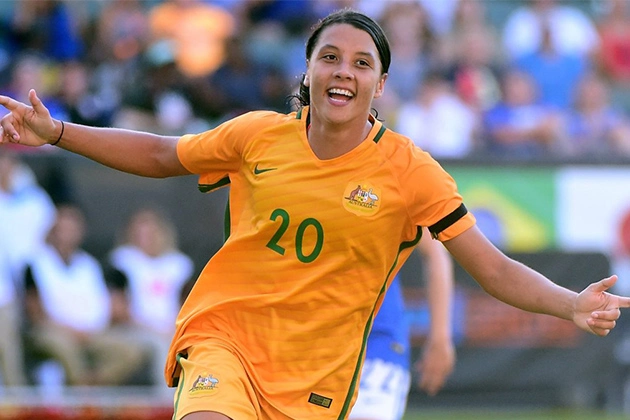

Prior to her retirement in August 2021, USA star Carli Lloyd earned more than £432,000 annually, according to SportBible. Sam Kerr of Australia and Chelsea is now believed to be the highest-paid player in the women’s game, earning more than £400,000 annually.
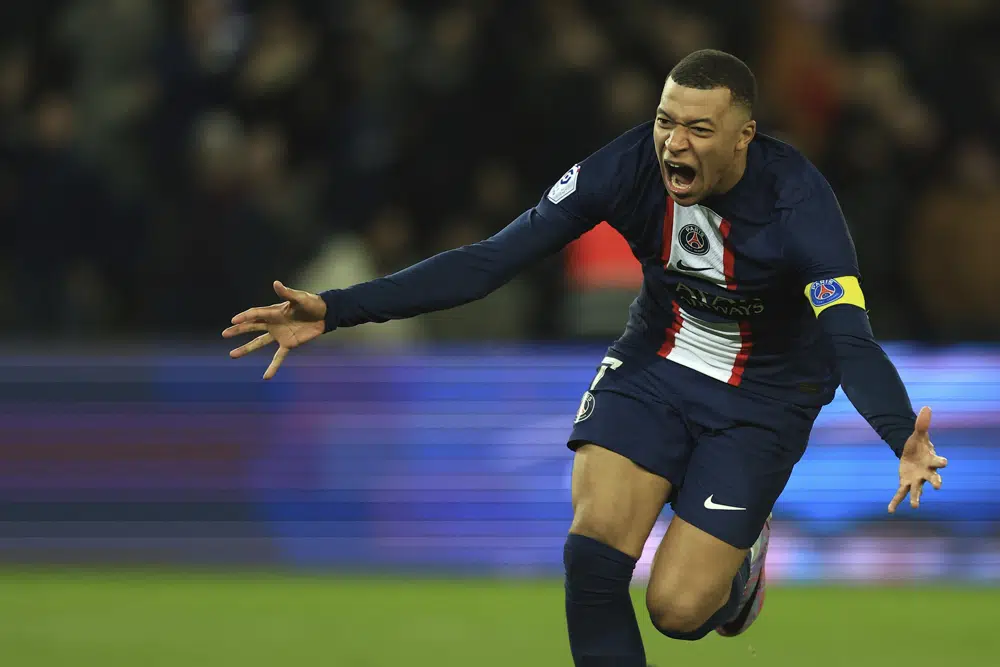

The highest paid footballer for the year 2022, however, is 23-year-old Kylian Mbappe, who earns $128 million (£115.2 million) every season.
Reasons for Gender Pay Gap in Soccer:
The reasons for the gender pay gap in soccer are complex and multifaceted. Historically, men’s soccer has been more popular and profitable than women’s soccer, which has led to greater investment and resources being directed towards men’s soccer. As a result, women’s soccer has not received the same level of investment and resources as men’s soccer, which has contributed to disparities in pay and opportunities.
One reason for this pay gap is that men’s soccer attracts more viewers, which translates into higher revenue from sponsorships, advertising, and ticket sales. Men’s soccer has been around for much longer than women’s soccer, and as a result, has had more time to build up a fan base and generate revenue. However, this does not fully explain the disparity in earnings between male and female players, as women’s soccer continues to grow in popularity and attract more viewers.
Another factor that contributes to the pay gap is the lack of investment in women’s soccer. Women’s teams are often underfunded and have fewer resources than men’s teams. This makes it difficult for female players to reach their full potential, and limits their earning potential. For example, women’s soccer players in some countries have to work part-time jobs in addition to playing soccer to make ends meet.
There are also issues related to cultural attitudes and biases towards women in sports. Societal norms and expectations around gender roles have often led to the marginalization and under-representation of women in sports, including soccer. This has created a perception that women’s sports are less important or valuable than men’s sports, which has further perpetuated the gender pay gap.
Measures for Achieving Gender Equality
Despite the challenges, there are steps being taken to address the gender pay gap in soccer. In some countries, such as Australia, Norway, and New Zealand, there are regulations in place that require equal pay for male and female national team players. In other countries, such as the United States, female national team players have taken legal action to fight for equal pay.
Another solution is to invest more in women’s soccer, including increasing the number of professional teams and providing more resources for female players. This would help to bring more attention to women’s soccer and increase its popularity, which could help to close the pay gap over time.
The Role of FIFA in Reducing the Gender Pay Gap in Soccer
FIFA has been working to address the gender pay gap in soccer by implementing policies aimed at promoting gender equality. In 2019, FIFA announced that it would increase the prize money for the 2019 Women’s World Cup from $30 million to $150 million, making it the largest ever prize money for a women’s soccer tournament.

Gianni Infantino, the president of FIFA, announced the prize money for the 2023 FIFA Women’s World Cup will grow by 300% to $150 million.
Although the prize money for the Women’s World Cup is now three times what it was in 2019 and ten times what it was in 2015—the year before Infantino was elected president of FIFA—it is still significantly less than the $440 million total prize money awarded at the men’s World Cup in Qatar last year.
Additionally, FIFA has launched initiatives such as the Women’s Football Development Program, which aims to provide support and resources to women’s football at the grassroots level, and the Women’s Football Strategy, which outlines FIFA’s vision for the future of women’s football. FIFA has also established a Women’s Football Division, which is responsible for overseeing and promoting women’s football within the organization. While there is still work to be done, these efforts by FIFA are a step towards closing the gender pay gap in soccer and promoting gender equality in the sport.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the gender pay gap in soccer is a complex issue that will not be solved overnight. However, by raising awareness, implementing regulations, and investing more in women’s soccer, we can work towards creating a more equitable and inclusive sport for all players, regardless of gender.
However, there has been progress in recent years, with organizations such as FIFA, national soccer federations, and individual clubs and leagues investing more in women’s soccer. Increasing public interest and support for women’s soccer has also helped to drive investment and growth in the sport.